EXPERIENCES IN THE LABORATORY
ABSORPTION OF LIGHT
remember that…
White light comprises three basic light colours: red, green and blue.
The basic pigment colours are cyan, magenta and yellow. These are obtained from combining two light colours, as shown in the image.
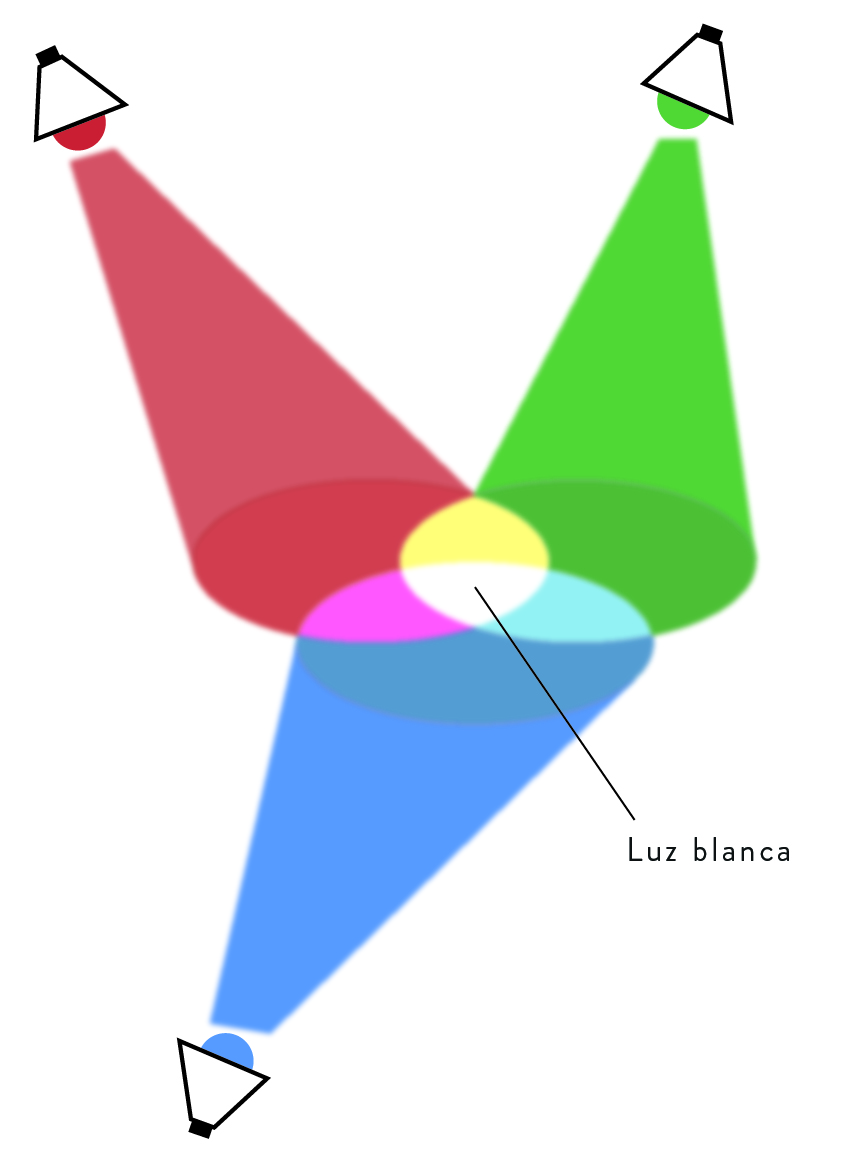
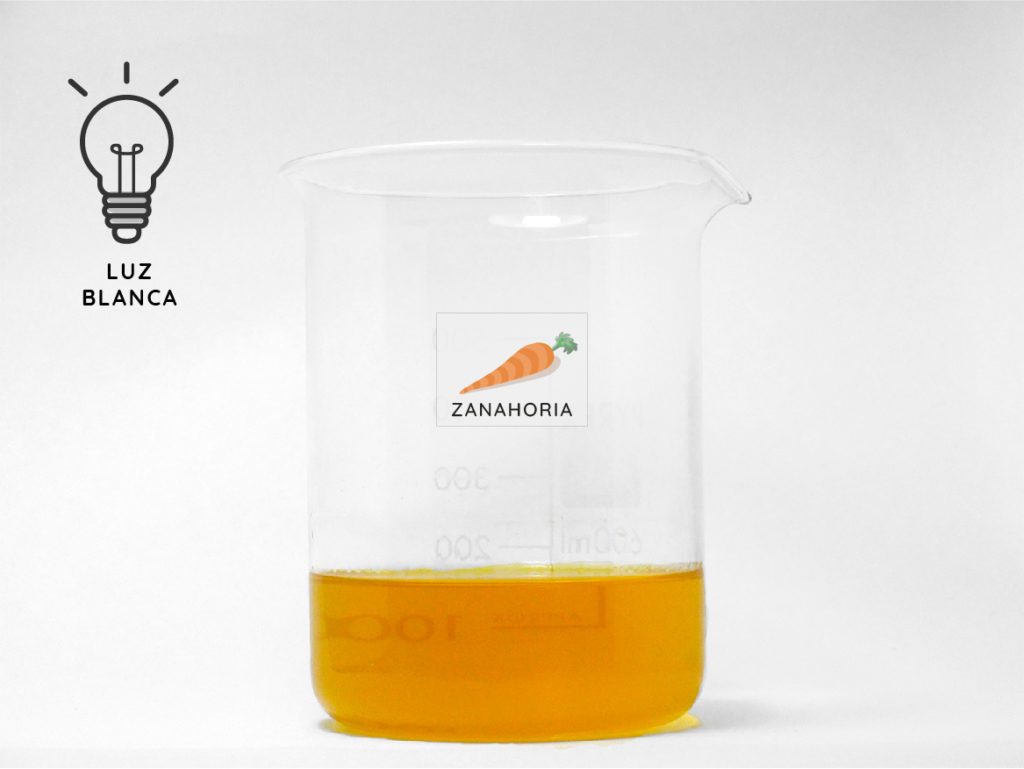
How do we know which light the pigment absorbs?
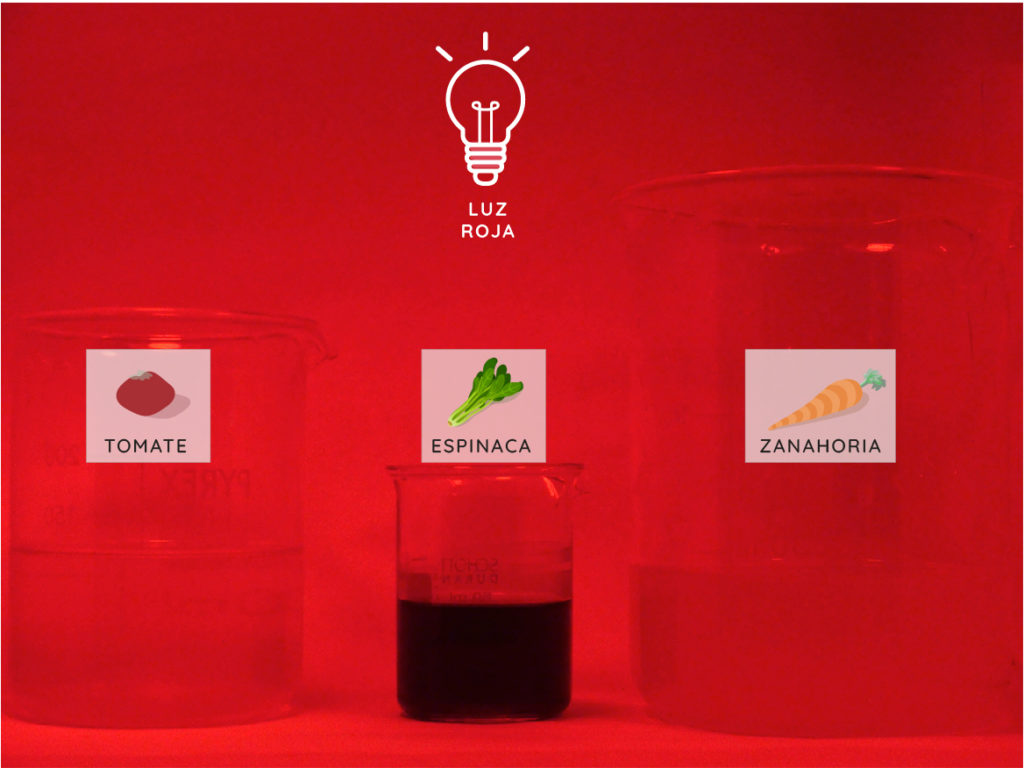
f we light tomatoes, carrots or spinach with the basic light colours red, green and blue, the pigment is transparent to the colour it does not absorb, which corresponds to the pigment colour we see. In contrast, the blacker the pigment looks, the more it will have absorbed the light colour we have lit it up with.
Comparing photosynthetic pigments: carotene in carrots and tomatoes and chlorophyll in spinach
How do they absorb the different pigments?
And what happens to the pigments of phytoplankton and seaweed?
The colour of the pigments shows us exactly which colours they do not absorb. The following table links the colour to the pigment present in seaweed.