Beagle group
Food source
Marine fauna has traditionally been exploited for food by different cultures, but overexploitation is currently threatening populations and affecting food webs.
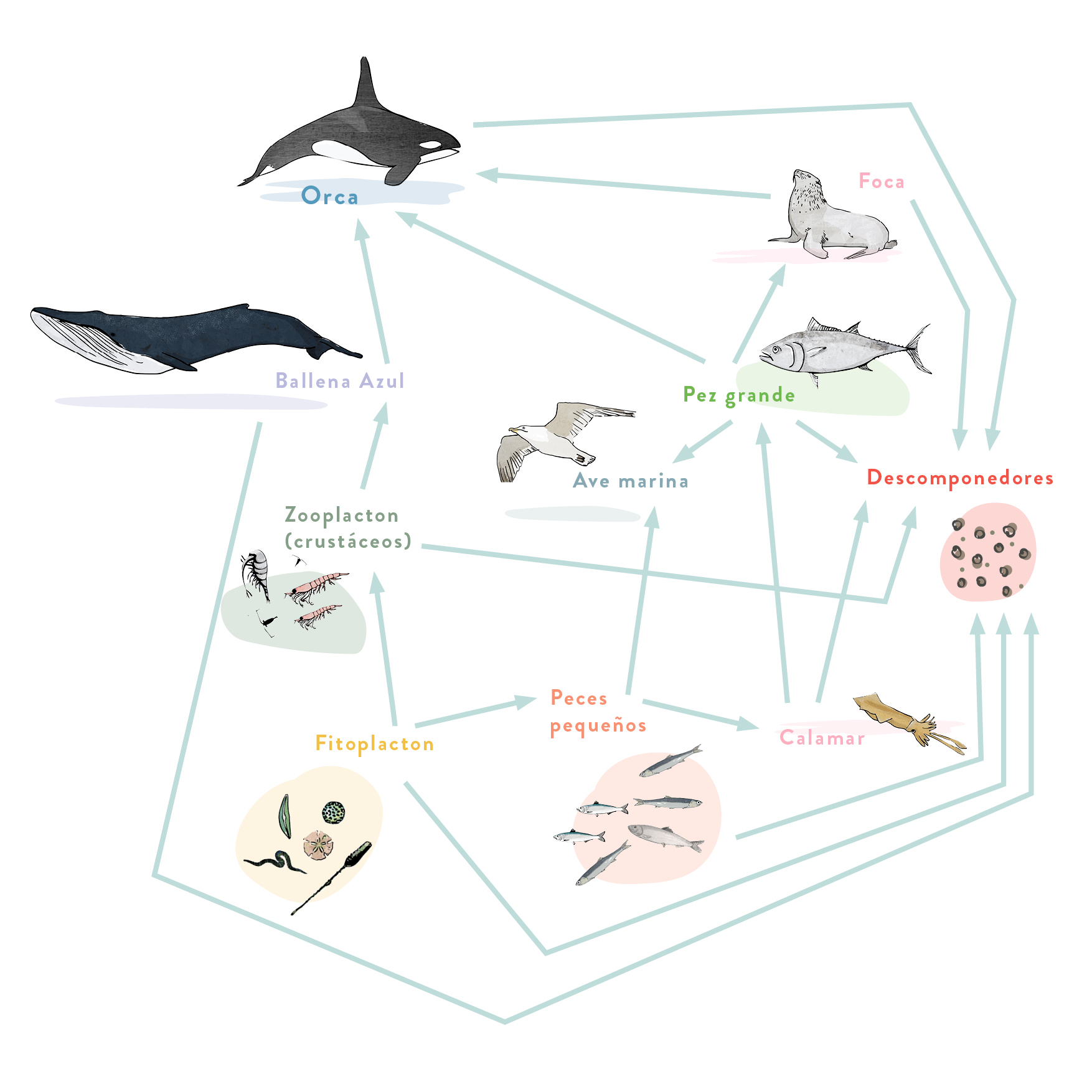
Overfishing of whales is leading these animals to the brink of extinction. There are many other fish whose populations have also been decimated by overfishing. The European Union establishes total acceptable catches (TACs) for most fish of commercial interest. EU countries must distribute the fishers’ national quotas and ensure they are not exceeded.
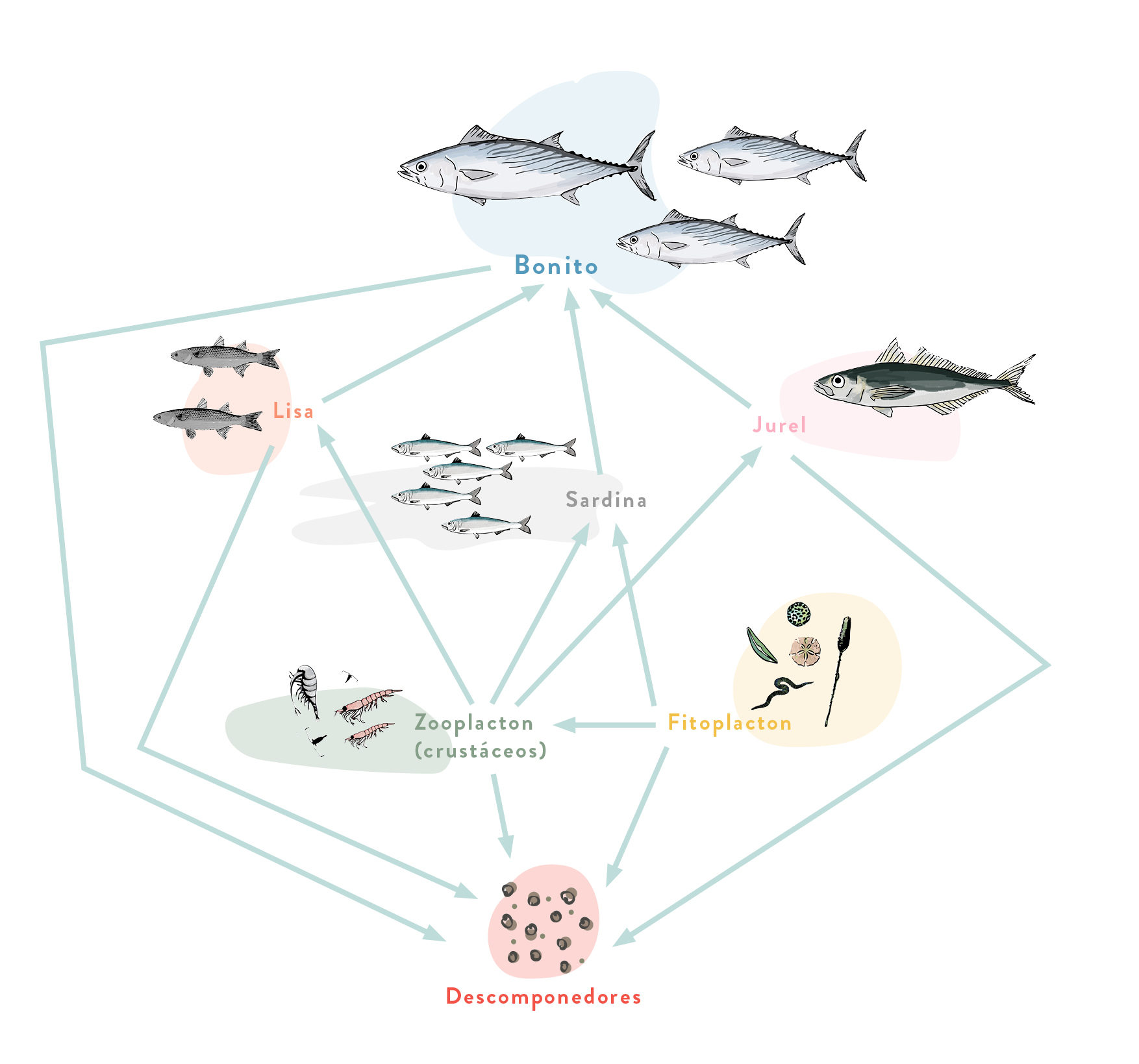
Overfishing is decimating bonito and whale populations. Compare the blue whale web to the bonito web.
If the fishing of these two organisms was prohibited, which of the two webs could recover more quickly? Why?
You can find the answer in the OCEAN: SOURCE OF FOOD sections where there are simplified food webs of the most commercial fish.
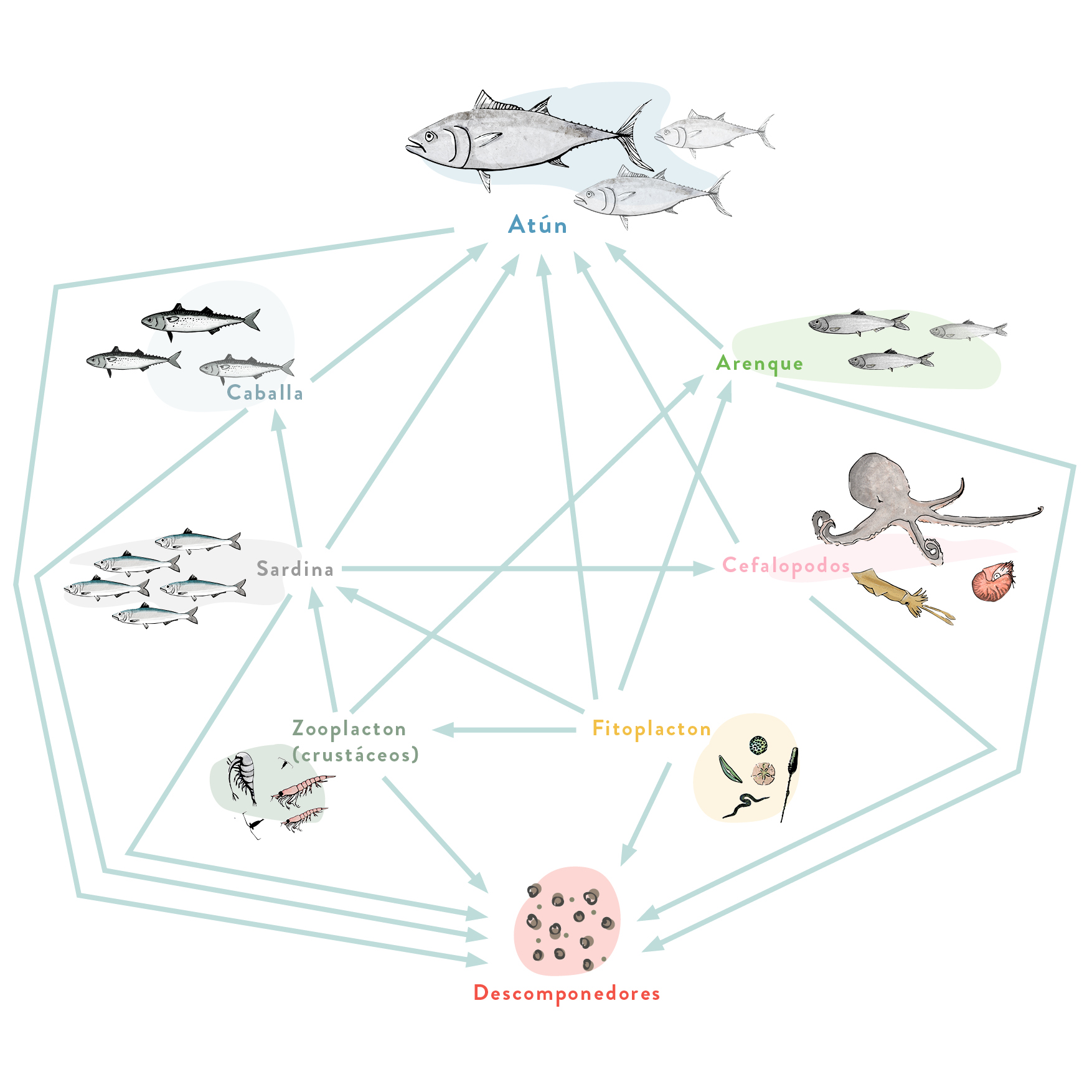
FOOD WEBS
TUNA
This is a pelagic species that can be found both near the sea surface and at a considerable depth. These fish are fast and active swimmers. Tuna periodically swim from the Atlantic to the Mediterranean to spawn and they return when spawning has ended.
They are predators that feed on fish (mackerel, herring, sardine), cephalopods and pelagic crustaceans.
These highly prized fish in economic terms are caught using several techniques: seining, longline, almadraba and with a fishing rod by sport fishers. They are also raised in fish farms.
How many trophic levels does the tuna web have?
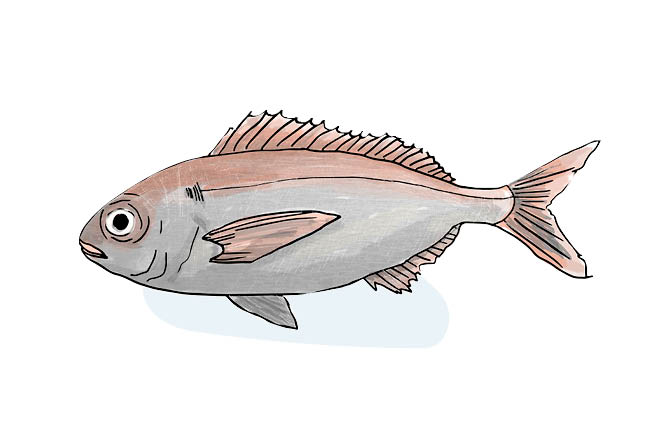
Sea bream
It is found in water up to 400 m deep. It is a gregarious species that feeds on invertebrates, crustaceans, molluscs and larvae or the juveniles of other fish.
Its flesh is highly prized and it is fished with longlines, trawl nets and occasionally with trammel nets. It is also a sportfishing species. Sea bream is also raised in fish farms.
How many trophic levels does the Sea bream have?
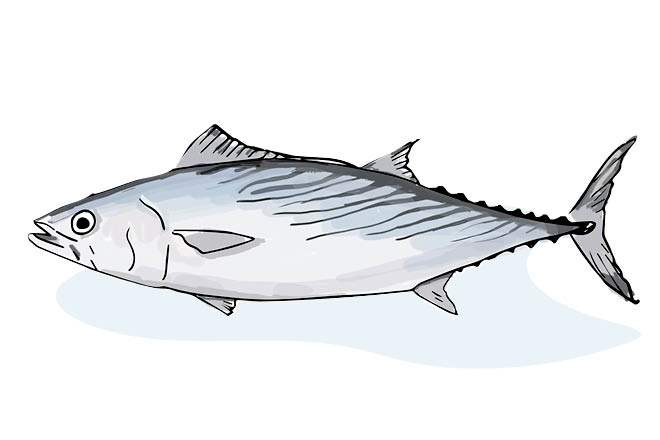
Bonito
Pelagic species involved in major migrations that often forms shoals near the surface. It mainly feeds on fish like sardine, horse mackerel and mullet.
It is fished all year round with various techniques depending on the season. For example, one of the most used in the Mediterranean is the surface longline.
In other areas it is also fished with troll nets or seining techniques.
The use of large drift nets is decimating bonito populations.
How many trophic levels does the Bonito have?

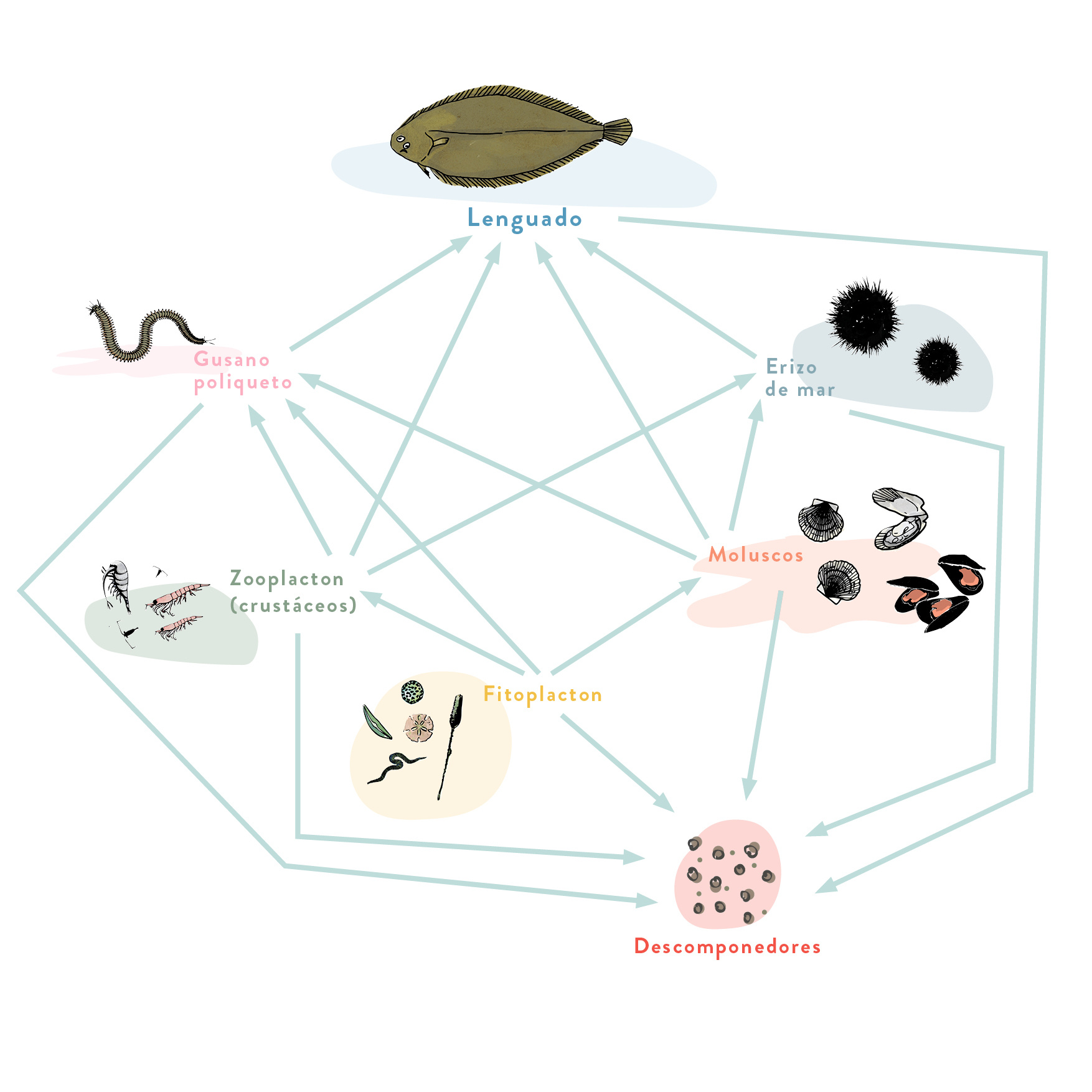
Sole
Fish that lives on sandy and muddy seabeds from the coast to 200 m. It buries itself during the day and feeds at night by catching benthic organisms.
It is fished with trammel or trawl nets. Sole is also raised in fish farms.
How many trophic levels does the Bonito have?

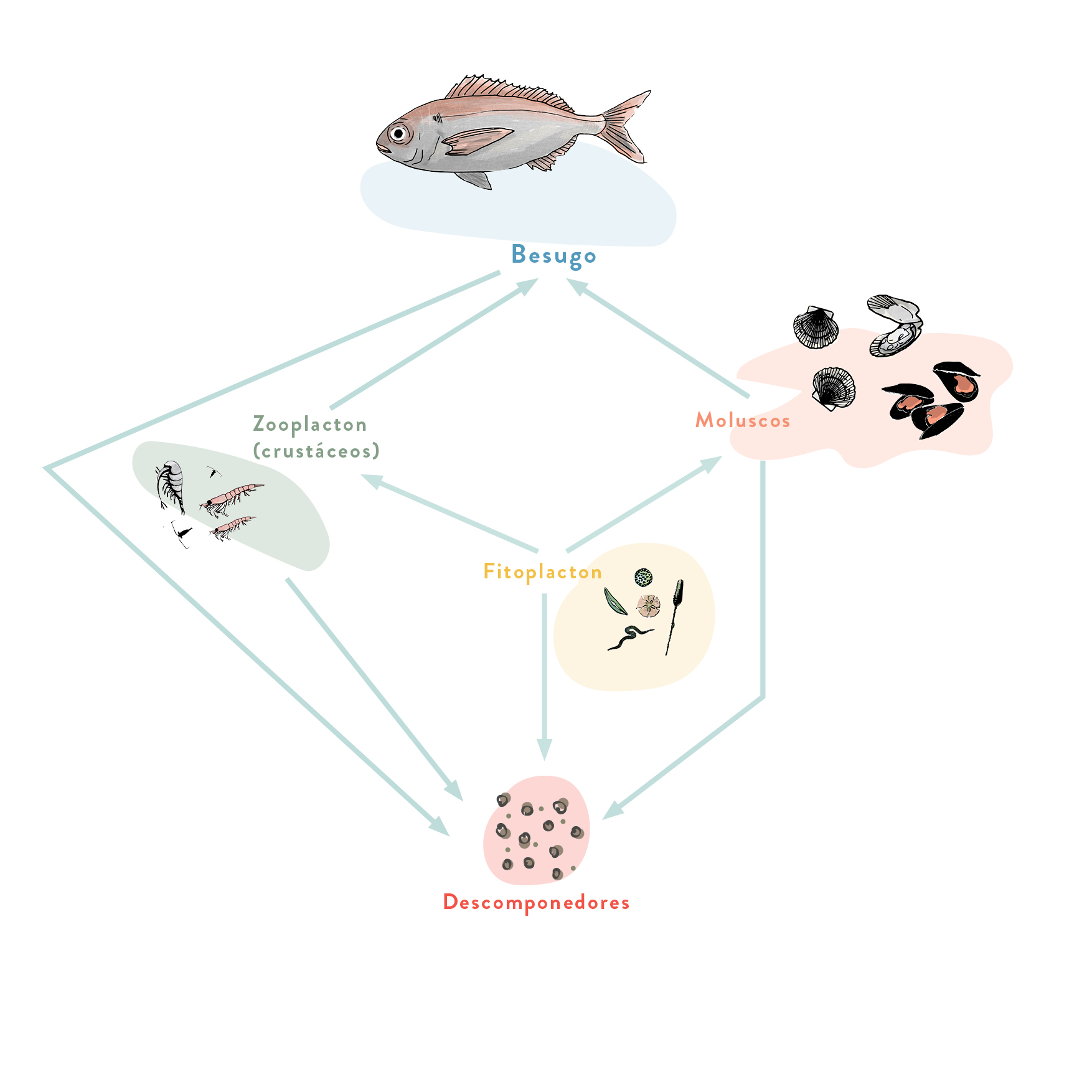
Sea bass
This species lives in shallow water. As juveniles, they are gregarious and form shoals. As adults, they become more solitary. They feed on fish, crustaceans and molluscs.
Species with excellent flesh that can reach a high price in the market. That is why they are sought after by both professional and sport fishers alike. Professionals catch them with trammel nets and longlines. They are also raised in fish farms.
How many trophic levels does the Sea bass have?
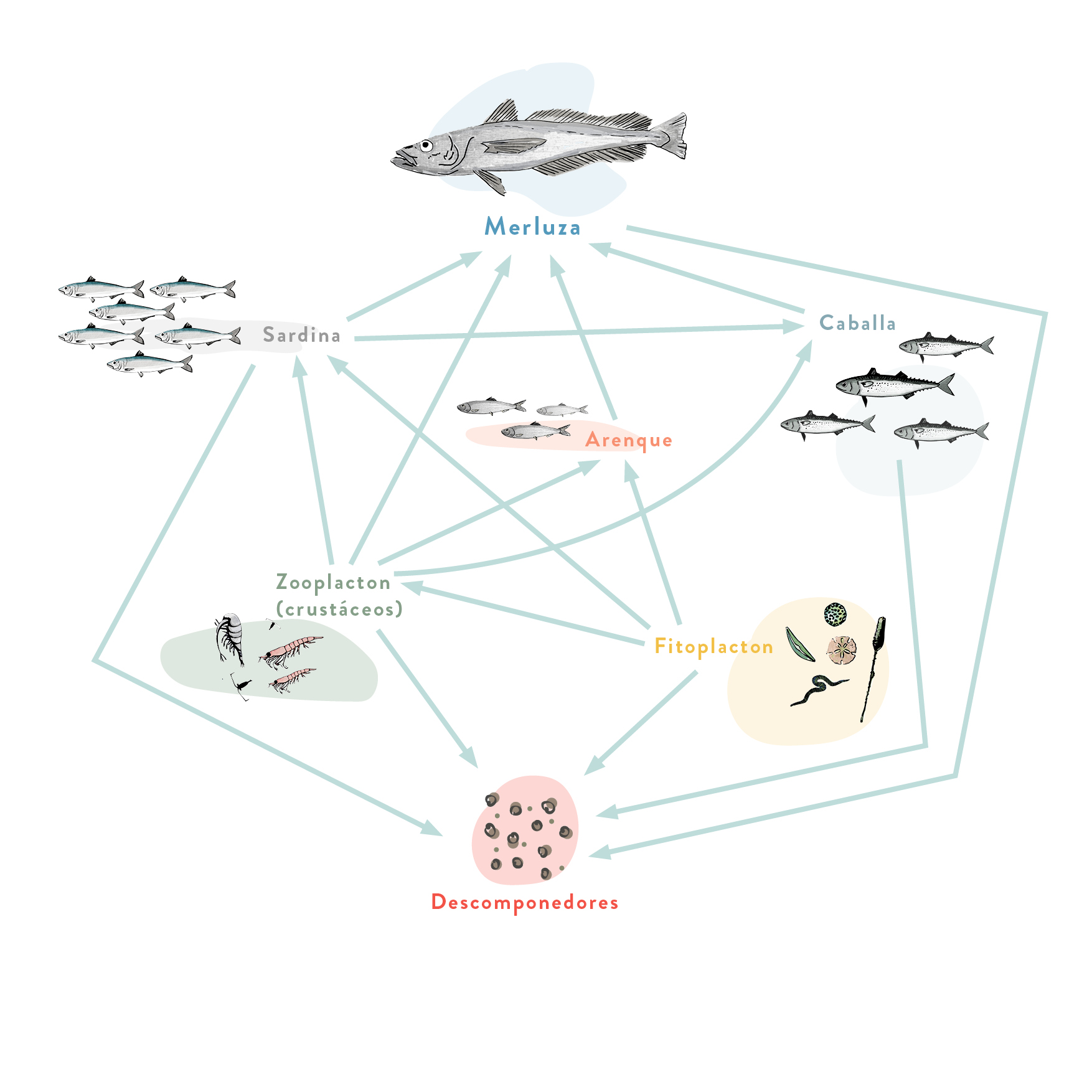
Hake
This species lives at a depth of 30–500 m. In winter it is found in deeper waters and in summer it swims close to the coast. It stays near the sea floor during the day and at night it comes to the surface to feed. It feeds on gregarious fish (sardine, herring, mackerel, sprat, anchovy, etc.) and crustaceans. It is one of the most important commercial species. It is fished in large quantities, around 5,000 tonnes, along the Mediterranean coasts of the Iberian peninsula.
It is mainly caught with trawl nets at depths of 50–500 m, and with longlines, at around 250 m, although sometimes the bottom longline goes to a depth of 1,000 m.
How many trophic levels does the Hake have?
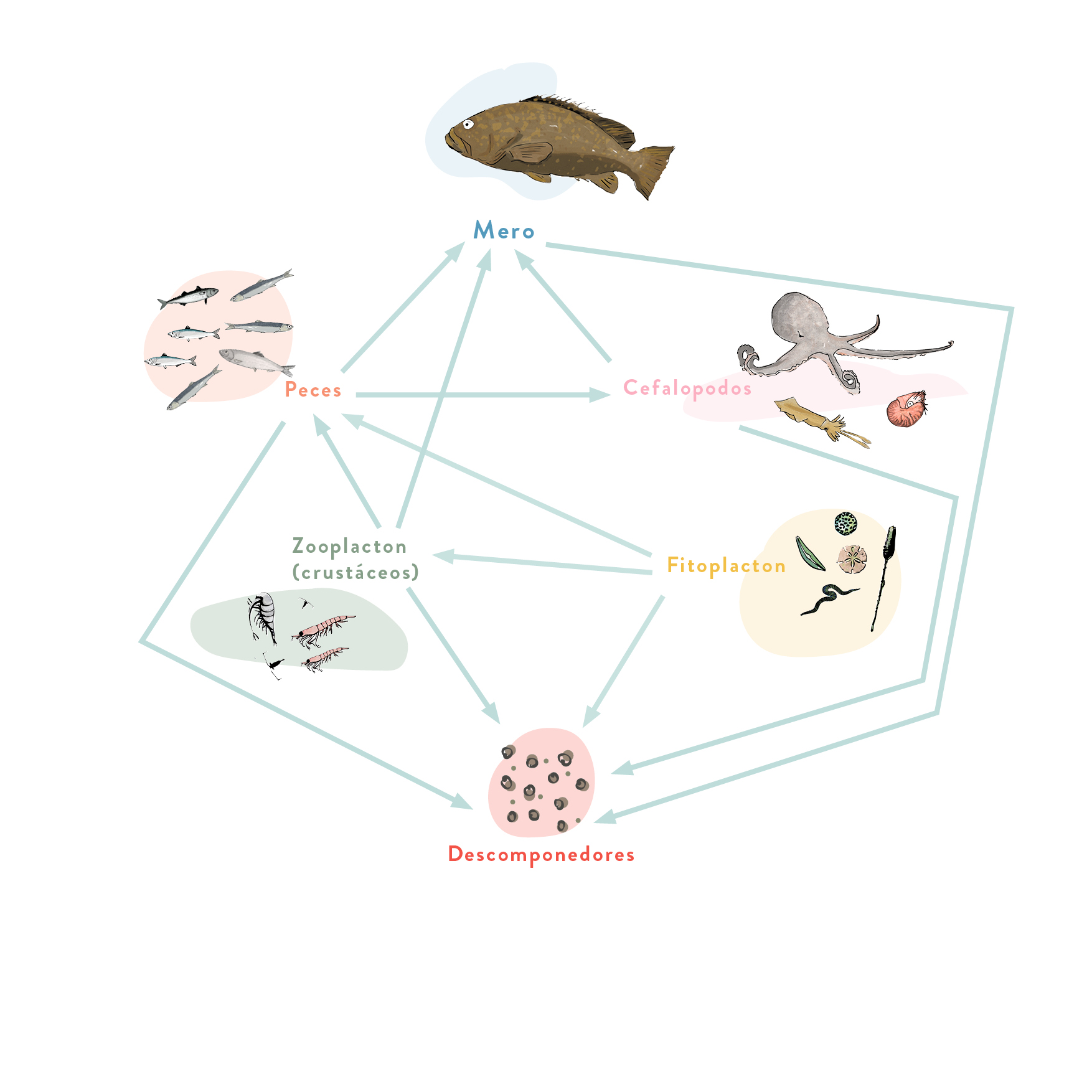
Grouper
Basically, a coastal fish that likes rocky seabeds formed by large blocks where it can find refuge. The depth at which it is found varies from 5 to 400 m depending on the fishing pressure level it is subjected to. It is the prime catch of spearfishing in the Mediterranean, which is the most effective system for catching this species. This fishing method is the reason why this species has almost disappeared from many of our coasts.
It mainly feeds on cephalopods and also crustaceans and several types of fish
How many trophic levels does the Grouper have?
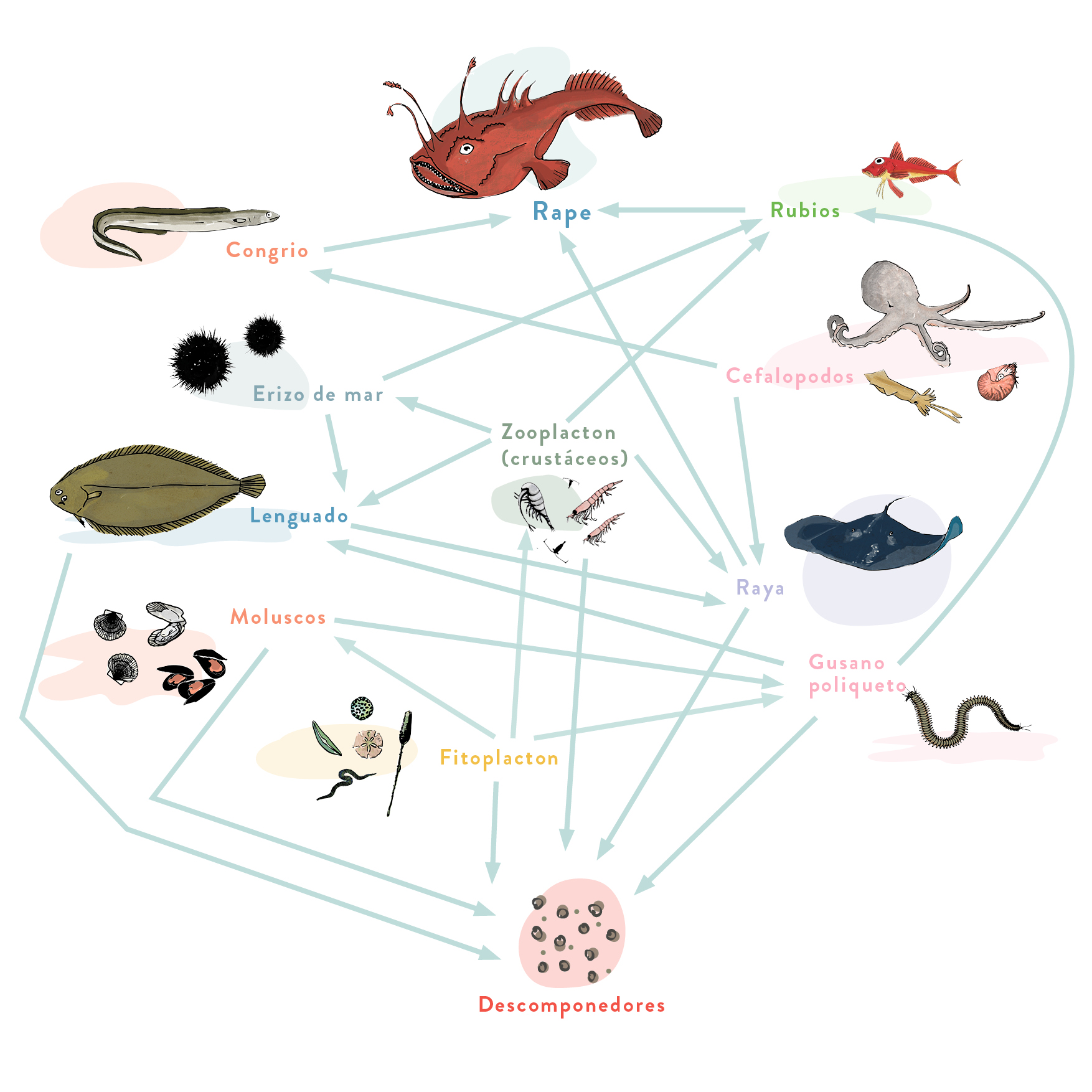
Monkfish
It lives close to the sea floor from the coastline to 500 m. Sometimes it is found half buried in muddy and sandy bottoms. It can also be observed between seaweed and rocks on sandy sea floors.
An extremely voracious fish that lies in wait for its prey. It feeds on other fish by attracting them by moving the fleshy ecsa on the end of its first dorsal fin ray. It may come to the surface where it sometimes attacks seabirds.
It is caught exclusively with the trawling technique.
How many trophic levels does the Monkfish have?
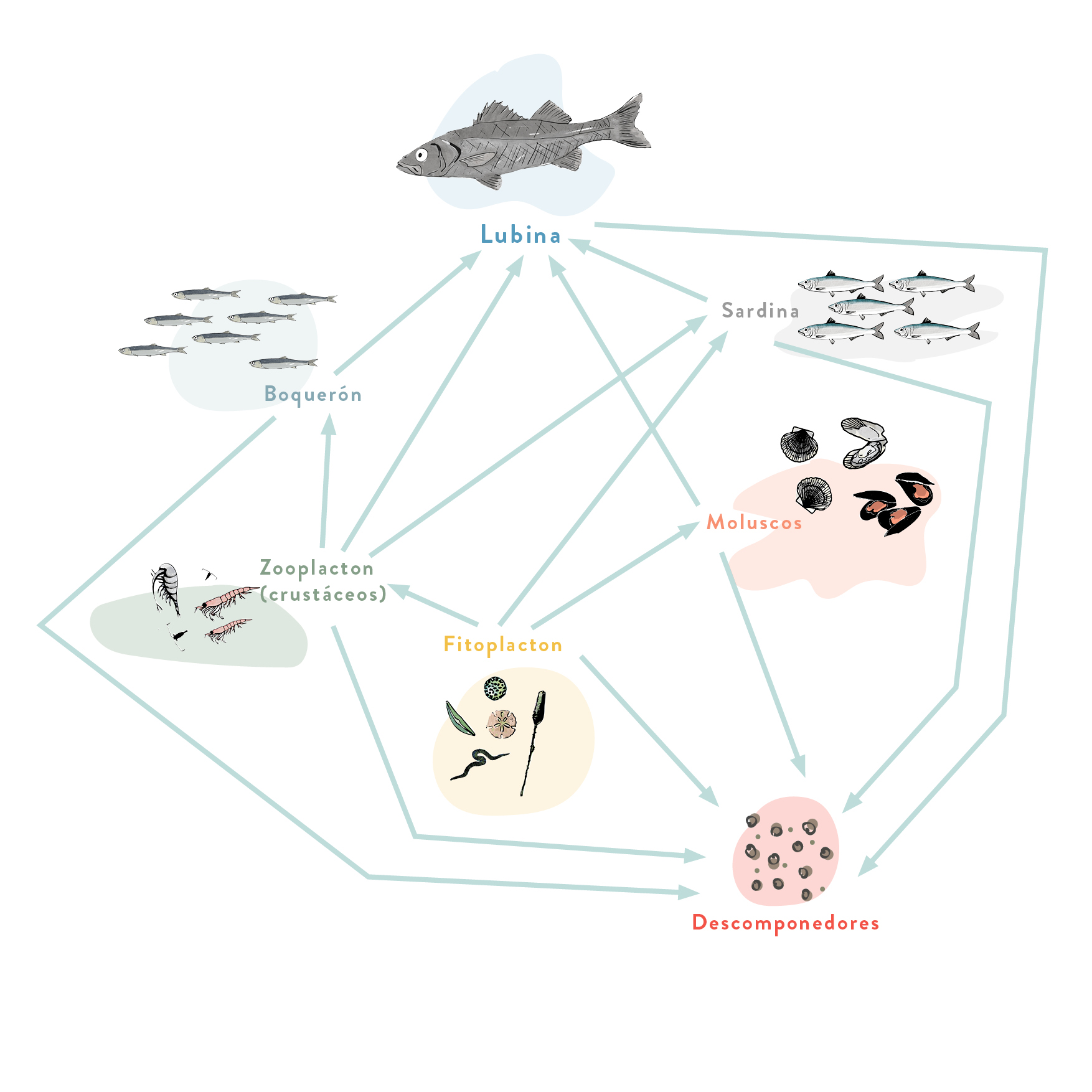
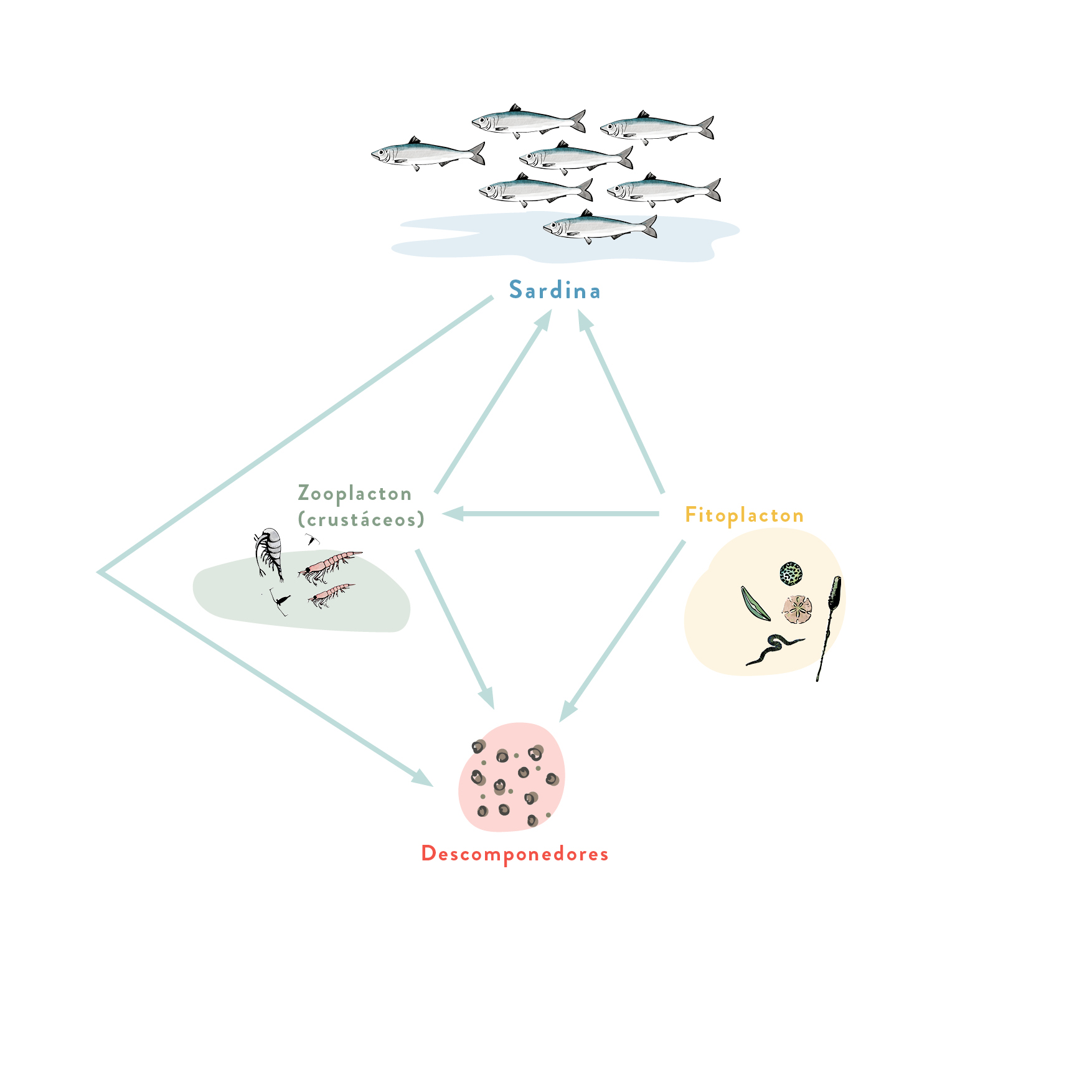
Sardine
This is a gregarious species whose large shoals can sometimes swim into brackish water. It is found in coastal waters at a depth of 15–50 m. It feeds on planktonic crustaceans and phytoplankton.
It is a highly prized species in commercial terms, and around 45,000 tonnes are caught in the north-western Mediterranean every year. Sardines are caught with seine and drift nets, mainly at night when they are attracted by artificial light. They are also caught using trawl nets.
How many trophic levels does the Sardine have?
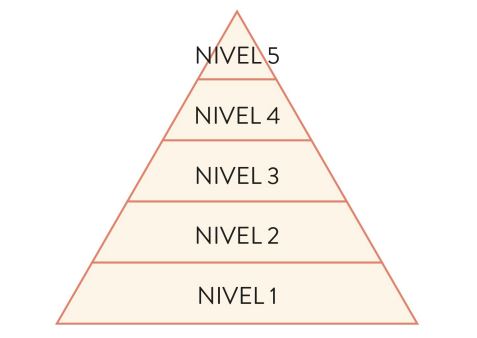
Why is the trophic organisation of a system represented by a pyramid, not a tower?
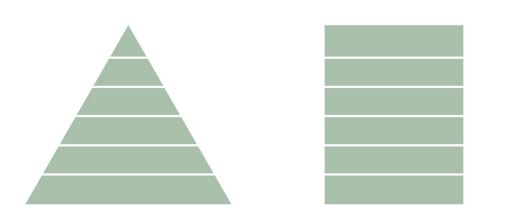
What are the reasons why the number of levels in a trophic pyramid is low?